Route53
Managed DNS
Route53 can USE:
·
Public domain names you own (or buy)
·
private domain names that can be
resolved by your instances in your VPCs
Route53 has
Advanced Features such as:
·
load Balancing (through DNS - also
called client load balancing)
·
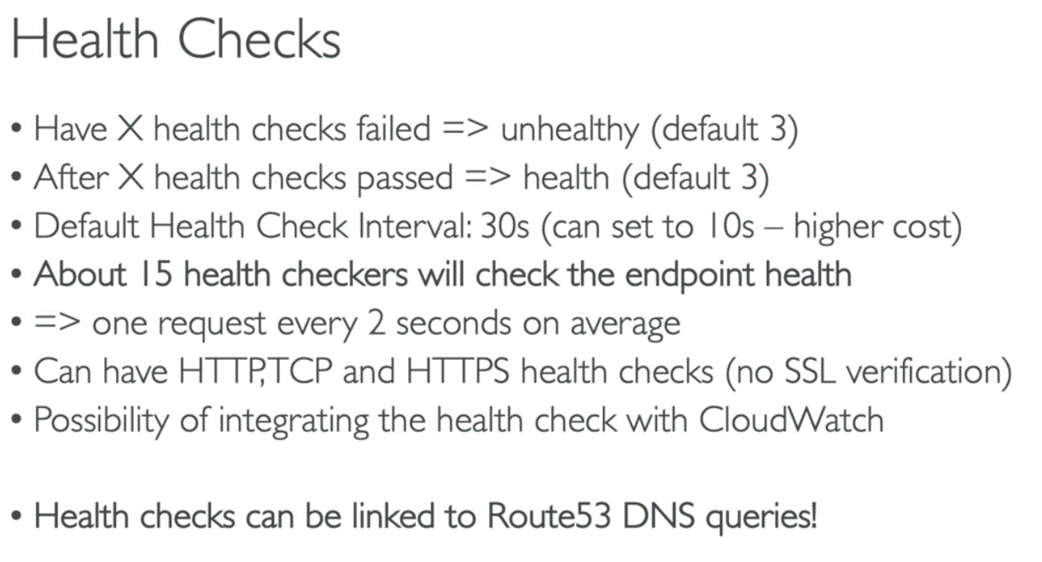
Health Checks (although limited )
·
pay 50 cents per month per hosted
Zone
·
CNAME vs
ALIAS
o AWS
Resources (Load Balancer and Cloudfront etc) expose asn
AWS URL lb12-1234.ap-southeast-2-elb.amazonaws.com and you want it to be
myapp.mydomain.com
o CNAME
§
Points an
URL to any other URL
§
Only for NonRoot Domain , Zone
Apex (aka something.mydomain.com)
o ALIAS
§
Points an
URL to an resource only.
(myapp.mydomain.com -> something.amazinaws.com)
§
Works for both Root and Non Root
domain (aka mydomain.com )
§
free of charge
§
Native health checks
Routing
Policies
·
Simple
o one
record can point to multiple IP addresses, where if multiple addresses are
entered in the record, any of the addresses are returned in random order.
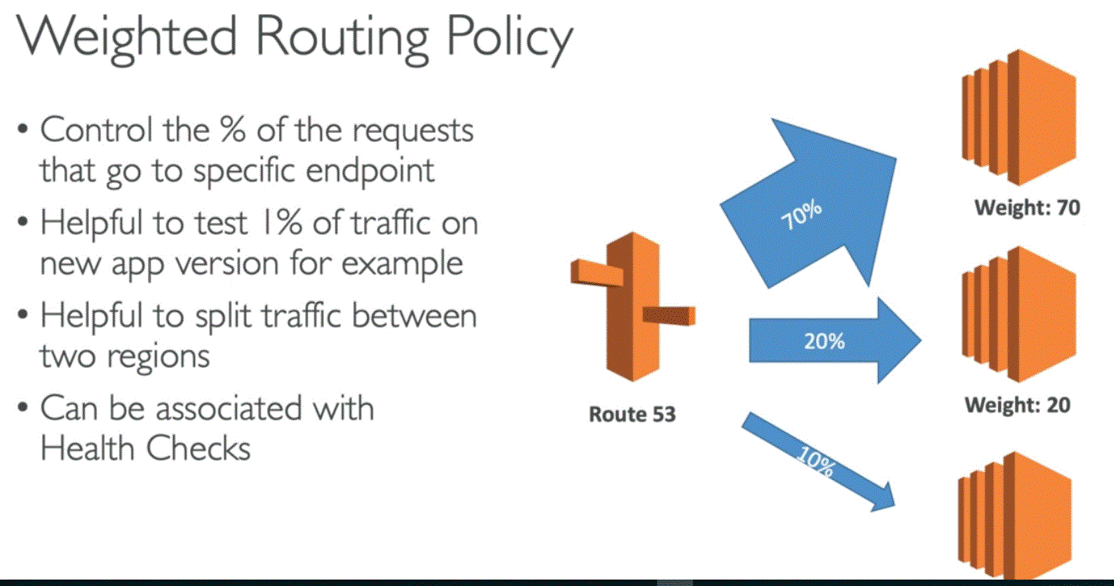
·
Weighted
o Add
each record separately with a particular weight; Route53 then apportions the
record set appropriately
o can
have health check
·
Latency
o Routes
to lowest latency for the user
·
Failover
o Primary
and Secondary records in the set. i.e. Active / Passive
o Health
check fails
·
Geolocation
o Route
based on user Geolocation
§
Geoproximity Routing Policy (Traffic Flow Only)
Ø
Route based on users and resources
Ø
Introduce bias (extend or shrink a
region)
Ø
·
Multi Value
o similar
to Simple Routing Policy but has health
checks
o Use
when routing Traffic to multiple resources
o Want
to associate health-checks with Records
o up
to 8 healthy records are returned with each Muti-Value
query
o Multi-Value
is not a substitute for having an ELB
A Route Origin
Authorization (ROA) is a document that you can create through your Regional
internet registry (RIR), such as the American Registry for Internet Numbers
(ARIN) or Réseaux IP Européens
Network Coordination Centre (RIPE). It contains the address range, the ASNs
that are allowed to advertise the address range, and an expiration date. Hence,
Option 3 is the correct answer.
The ROA authorizes Amazon to advertise an address
range under a specific AS number. However, it does not authorize your AWS account
to bring the address range to AWS. To authorize your AWS account to bring an
address range to AWS, you must publish a self-signed X509 certificate in the
RDAP remarks for the address range. The certificate contains a public key,
which AWS uses to verify the authorization-context signature that you provide.
You should keep your private key secure and use it to sign
DNS > CNAME point to subdomain
| Alias can point to apex | CNAME is a Canonical Name Record or Alias Record
that specifies that one domain name is an alias of another canonical domain
name.
A Record is used to point a logical domain name, such
as "google.com", to the IP address of Google's hosting server,
"74.125.224.147".
Private DNS Route53 > Private hosted Zone with dns resolution
the authorization-context message.
DNS
records consist of;
-A (address record) the IP address eg; 192.168.0.1
-AAAA (IPv6 address record)
-CNAME (canonical name
record)
-CAA (certification authority authorization)
-MX (mail exchange record)
-NAPTR (name authority pointer record)
-NS (name server record)
-PTR (pointer record) ; ised
for reverse lookup , i.e opposite of "A"
record
-SOA (start of authority record)
-SPF (sender policy framework)
-SRV (service locator)
-TXT (text record)