AWS ELASTIC
LOAD BALANCING - ELB
·
Distributes incoming application or
network traffic across multiple targets, such as EC2 instances, containers ECS, and IP addresses, in multiple Availability Zones.
·
When you create a load balancer, you must
specify one public subnet from at least two Availability Zones. You can specify
only one public subnet per AZ
GENERAL
FEATURES
·
Accepts incoming traffic from clients
and routes requests to registered targets.
·
Monitors the health of its registered
targets and routes traffic only to healthy targets.
·
Enable deletion protection to prevent
your load balancer from being deleted accidently. Disabled by default.
·
Deleting ELB wont delete the
instances registered to it
·
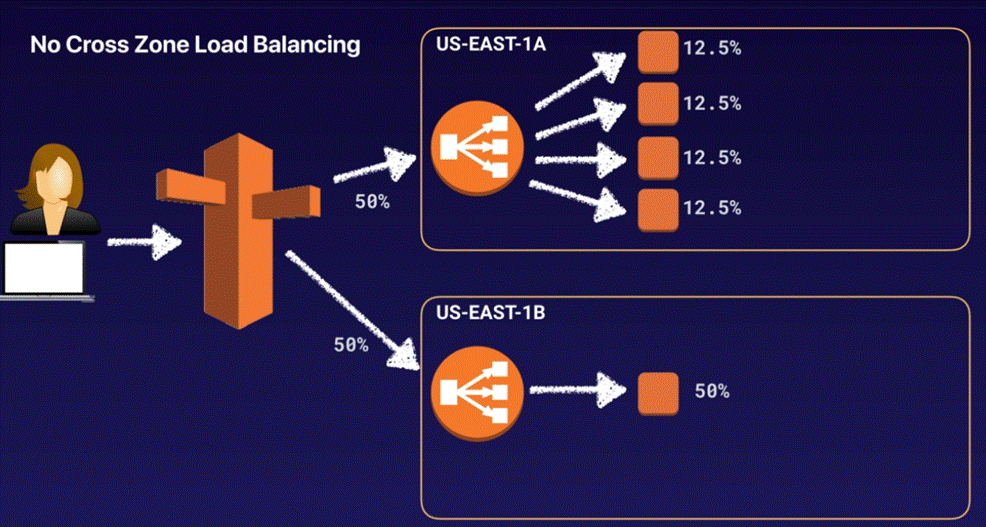
Cross
Zone Load Balancing - when enabled, each load balancer
node distributes traffic across registered targets in all enabled AZs
Three Types
of Load Balancers
·
Application
Load Balancer
o
Functions at the application layer,
the seventh layer of the Open
Systems Interconnection (OSI) model
o
Allows HTTP and HTTPS
o
At least 2 subnets must be specified
when creating this type of load balancer.
o
Components
§
A load
balancer servers as the single point of contact for clients
§
A listener
checks for connection requests from clients. You must define a default rule for
each listener that specifies a target group, condition, and priority
§
Target
group routes requests to one or more registered targets.
You can register with multiple targets groups, and configure health checks on a
per target group basis.
o
Benefits
§
Support for path based and host based
routing
§
Support for routing requests to
multiple applications on a single EC2 instance
§
Support for registering targets by IP
address, including targets outside of the VPC for the load balancer
§
Support for containerized applications
§
Support for monitoring the health of
each service independently
o
Cross-Zone load Balancing is always
enabled (no cross zone)
o
If you specify targets using instance ID traffic is routed using the
private IP address specified in the primary network interface of the instance.
If you specify targets using IP
addresses you can route traffic to an instance using any private IP address
from one or more network interfaces
o
Supports load balancer generated
cookies only for sticky sessions
o
HTTP/2 support
o
Web sockets Support
o
Monitoring
§
CloudWatch metrics -retrieve
statistics about data points for your load balancers and targets as an ordered
set of time-series data, known as metrics
§
Access logs - capture detailed
information about requests made to your load balancer and store them as log
files in S3
§
Request tracing - track HTTP requests
§
CloudTrail logs - capture detailed
information about calls made to the ELB API and store them in S3
·
NETWORK
LOAD BALANCER
o
Static IP can be address can be
provided; 1 per subnet
Nlb > tcp, can see the
client IP , must attach an EIP (if public facing) otherwise a random IP will be
created and assigned, cross zone load balancing -> SSL Termination
SSE can be used with SQS,
·
ELB
Monitoring Types
o Cloudwatch
Metrics - health / Performance
§
BackEndConnectionErrors -> number
of unsuccessful connections to backend instances
§
HealthyHostCount -> number of healthy
instances registered
§
unHealthyHostCount -> number of unhealthy
instances registered
§
HTTP
Backend 2xx, 3xx, 4xx & 5xx
§
Latency
-> number of seconds taken from registered instance to respond / connect
§
Request
Count -> number of requests completed during the
specified interval ( 1 or 5 mins )
§
SurgeQueueLength -> number of Pending
requests, max queue size is 1024 , additional requests get rejected ( Classic
Only)
§
SpillOverCount -> number of requests rejected
because the surge queue is full (classic only)
o Access
/ ELB logs - who is accessing the site
§
can store data in S3 that has been
deleted by the instance i.e 5xx etc, days after the
event
o Request
Tracing - ALB only - trace the connection internally to the AWs endpoint
o CloudTrail
Logs - who provisioned the ELB etc
·
ELB
Other
o If
expecting a sudden rise in traffic, contact AWS to pre-warm the ELB